Content from Introduction
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Overview
Questions
- Why use version control in official statistics?
Objectives
- Identify uses and purposes for using Git in official statistics
Version Control in General
Version control is important whether you are working alone or collaboratively, even if you are not working in statistics!
Here’s the basics of how a version control system works:
- start with a base version of a document
- record changes made each step of the way
- collaborators can add changes in independently without conflict
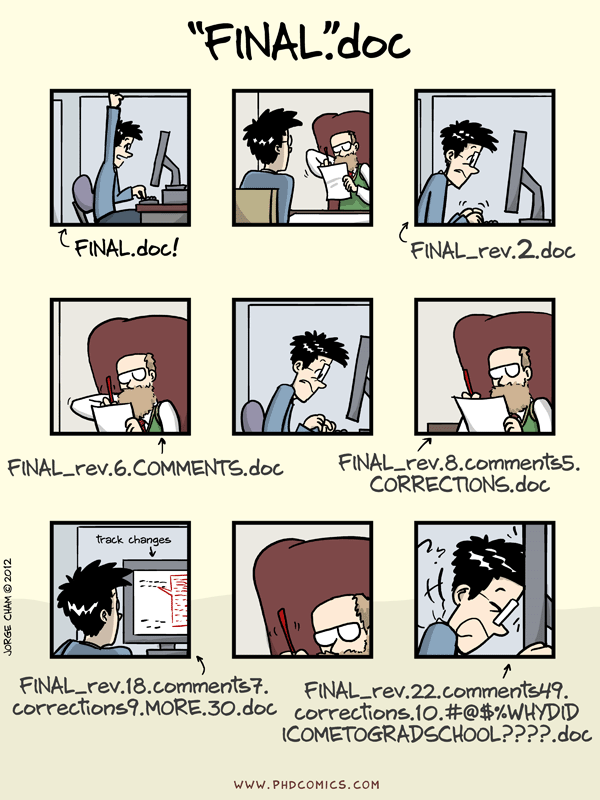
You’ve probably already seen a version control system.
Good version control systems will allow you to see the history of a project and will sync across different computers, facilitating collaboration.
Version Control Systems
What version control systems have you likely already come across? List 1-2
You’ve probably seen Microsoft’s Track Changes and Google Doc’s version history
Why Version Controlling Matters in Official Statistics
There are a number of reasons why version control matters matters in official statistics:
Reproducibility: Within and across organizations, we need to be able to reproduce statistics. This could be to ensure consistency in methodology across reference periods, or check to see if statistics are comparable in their methodologies.
Standardization: We can use version control systems as a single source of truth to create standardization of statistics between and within organizations.
Disseminate changes and updated versions: Following our single source of truth, we can easily update and share changes to calculations of official statistics as well as any new documentation or methodologies. This means we are updating in one place rather than many.
Collaboration: Version control systems allow us to collaborate and connect on the creation of official statistics internally and externally with stakeholders. We can use these systems to share proposed changes, share work, and test code.
Efficient and Effective Development of Code: With a single source of truth, we know exactly where to propose and find changes code that makes our statistics. In addition, many version control systems have project management or feedback tools that we can leverage to bundle communication and discussion with the code itself rather than working in multiple systems. This can allow for faster feedback and proposed updates.
Content from Version Control
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Overview
Questions
- What is Git?
- Why should I use it?
- How does it relate to open statistics?
Objectives
- Identify key concepts in version control and its use in official statistics
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Setting up Git
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 5 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I set up Git?
Objectives
- Configure basic settings in Git
Before we start using Git for the first time on a new computer, there are some things we need to set up. In this lesson, we will:
- Add a name and email address
- Set the text editor used for writing commit messages
- Understand the difference between
--globaland--localconfiguration - View/confirm configuration settings
We will be using Git Bash, the command line interface for Git.
Configure Name and Email
An important first step in using Git is adding your name and email. This information will be attached to commits, branches, and other changes you make in the future. This identifiability and accountability for code changes is one of the key benefits to using Git.
At the Git Bash prompt, enter the following, substituting your full
name for the name in quotation marks after user.name and
your email for the email address following user.email.
BASH
$ git config --global user.name "Jane Doe"
$ git config --global user.email "doe_jane@agency.gov"Your situation may vary, but if you are writing code in your official capacity and using an agency repository, you will most likely want to use your official email address and the one associated with your account on GitHub, GitLab, or other code sharing site.
Configure Text Editor
This is optional. By default, Git Bash will use the Vim text editor.
There are many different Git clients and ways of interacting with Git on your computer. Some clients have a full user interface that you use for selecting files to stage for commits and authoring commit messages. Others, like Git Bash, have a command line interface so when you want to write a lengthy commit message, it needs to call up a text editor.
The default text editor for Git Bash is Vim which has a reputation for being difficult, especially for new users. So you may want to change to something easier to use or something you are more familiar with (e.g., your favorite text editor).
To switch to one of the following editors in the tables below, you can use the associated configuration commands.
The nano text editor is packaged with Git Bash and Notepad is included in the Windows operating system.
| Editor | Configuration command |
|---|---|
| nano | $ git config --global core.editor "nano -w" |
| Notepad (Win) | $ git config --global core.editor "c:/Windows/System32/notepad.exe" |
The text editors below are not available by default, but you may be available to you. Setup for these is more complex because it requires providing a filepath to the program executable which may not be the same for everyone.
| Editor | Configuration command |
|---|---|
| Notepad++ (Win, 64-bit install) | $ git config --global core.editor "'c:/program files/Notepad++/notepad++.exe' -multiInst -notabbar -nosession -noPlugin" |
| Sublime Text (Win, 64-bit install) | $ git config --global core.editor "'c:/program files/sublime text 3/sublime_text.exe' -w" |
| VS Code | $ git config --global core.editor "code --wait" |
If you ever want to switch back to Vim as the default, you can run the following command.
| Editor | Configuration command |
|---|---|
| Vim | $ git config --global core.editor "vim" |
Exiting Vim
Vim is surprisingly difficult to exit from. If you wish to exit a
session without saving your changes, press Esc then type
:q! and hit Enter or ↵. If you want
to save your changes and quit, press Esc then type
:wq and hit Enter or ↵.
--global vs. --local
In the code samples above, we have used the --global
flag. These are the settings Git will use for all repositories on your
computer. As your use of Git becomes more complex, you may wish to have
different configuration settings for different repositories. This is
when you might use the --local flag. --local
allows you to set configuration for specific repositories.
To set local configuration, open Git Bash and navigate to the
repository you want to configure. You can then use the commands above,
but substitute --local for --global.
For example, if you want to set a different name or email address for a specific project, you can do so with commands like those below.
BASH
$ git config --local user.name "Jane R Doe"
$ git config --local user.email "janedoe@example.com"These settings will override the --global configuration
settings for that repository only.
View/Confirm Configuration
You may wish to check your configuration settings.
To see all configuration settings, you can use the following command. If you are in a repository, this will show all global and local configuration settings.
To view global settings only (Note: This command can be run anywhere):
To view local settings only (Note: This has to be run while in a repository):
To view specific settings, include the setting name. For example, to view the email address configuration setting:
Other Configuration Settings
There are other, optional configuration settings you may wish to change. Review Git documentation and consult with others on your team about other settings.
- Use
git configwith the--globaloption to configure a user name, email address, editor, and other preferences once per machine. - Use
--localin place of--globalwithin a repository to set repository specific changes.
Content from Creating a Repository
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Overview
Questions
- Where does Git store information?
Objectives
- Create a repository in a local folder
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Tracking Changes
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 20 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I record changes in Git?
- How do I check the status of my version control repository?
- How do I record notes about what changes I made and why?
Objectives
- Check the history of a file
- Use add and commit to record changes
- Create commit messages that are descriptive
Note This lesson has been adapted from Lesson 4 of Version Control with Git
Getting Started
First let’s make sure we’re still in the right directory. You should
be in the planets directory.
Let’s create a file called mars.txt that contains some
notes about the Red Planet’s suitability as a base. We’ll use
nano to edit the file; you can use whatever editor you
like. In particular, this does not have to be the
core.editor you set globally earlier. But remember, the
bash command to create or edit a new file will depend on the editor you
choose (it might not be nano). For a refresher on text
editors, check out “Which
Editor?” in The Unix Shell
lesson.
Type the text below into the mars.txt file:
OUTPUT
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite colorLet’s first verify that the file was properly created by running the
list command (ls):
OUTPUT
mars.txtmars.txt contains a single line, which we can see by
running:
OUTPUT
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite colorIf we check the status of our project again, Git tells us that it’s noticed the new file:
OUTPUT
On branch main
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
mars.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)The “untracked files” message means that there’s a file in the
directory that Git isn’t keeping track of. We can tell Git to track a
file using git add:
and then check that the right thing happened:
OUTPUT
On branch main
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: mars.txt
Git now knows that it’s supposed to keep track of
mars.txt, but it hasn’t recorded these changes as a commit
yet. To get it to do that, we need to run one more command:
OUTPUT
[main (root-commit) f22b25e] Start notes on Mars as a base
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 mars.txtWhen we run git commit, Git takes everything we have
told it to save by using git add and stores a copy
permanently inside the special .git directory. This
permanent copy is called a commit
(or revision) and its short
identifier is f22b25e. Your commit may have another
identifier.
We use the -m flag (for “message”) to record a short,
descriptive, and specific comment that will help us remember later on
what we did and why. If we just run git commit without the
-m option, Git will launch nano (or whatever
other editor we configured as core.editor) so that we can
write a longer message.
[Good commit messages][commit-messages] start with a brief (<50
characters) statement about the changes made in the commit. Generally,
the message should complete the sentence “If applied, this commit will”
If we run git status now:
OUTPUT
On branch main
nothing to commit, working tree cleanit tells us everything is up to date. If we want to know what we’ve
done recently, we can ask Git to show us the project’s history using
git log:
OUTPUT
commit f22b25e3233b4645dabd0d81e651fe074bd8e73b
Author: Vlad Dracula <vlad@tran.sylvan.ia>
Date: Thu Aug 22 09:51:46 2013 -0400
Start notes on Mars as a basegit log lists all commits made to a repository in
reverse chronological order. The listing for each commit includes the
commit’s full identifier (which starts with the same characters as the
short identifier printed by the git commit command
earlier), the commit’s author, when it was created, and the log message
Git was given when the commit was created.
Where Are My Changes?
If we run ls at this point, we will still see just one
file called mars.txt. That’s because Git saves information
about files’ history in the special .git directory
mentioned earlier so that our filesystem doesn’t become cluttered (and
so that we can’t accidentally edit or delete an old version).
Now suppose Dracula adds more information to the file. (Again, we’ll
edit with nano and then cat the file to show
its contents; you may use a different editor, and don’t need to
cat.)
OUTPUT
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite color
The two moons may be a problem for WolfmanWhen we run git status now, it tells us that a file it
already knows about has been modified:
OUTPUT
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: mars.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")The last line is the key phrase: “no changes added to commit”. We
have changed this file, but we haven’t told Git we will want to save
those changes (which we do with git add) nor have we saved
them (which we do with git commit). So let’s do that now.
It is good practice to always review our changes before saving them. We
do this using git diff. This shows us the differences
between the current state of the file and the most recently saved
version:
OUTPUT
diff --git a/mars.txt b/mars.txt
index df0654a..315bf3a 100644
--- a/mars.txt
+++ b/mars.txt
@@ -1 +1,2 @@
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite color
+The two moons may be a problem for WolfmanThe output is cryptic because it is actually a series of commands for
tools like editors and patch telling them how to
reconstruct one file given the other. If we break it down into
pieces:
- The first line tells us that Git is producing output similar to the
Unix
diffcommand comparing the old and new versions of the file. - The second line tells exactly which versions of the file Git is
comparing;
df0654aand315bf3aare unique computer-generated labels for those versions. - The third and fourth lines once again show the name of the file being changed.
- The remaining lines are the most interesting, they show us the
actual differences and the lines on which they occur. In particular, the
+marker in the first column shows where we added a line.
After reviewing our change, it’s time to commit it:
OUTPUT
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: mars.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")Whoops: Git won’t commit because we didn’t use git add
first. Let’s fix that:
OUTPUT
[main 34961b1] Add concerns about effects of Mars' moons on Wolfman
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)Git insists that we add files to the set we want to commit before actually committing anything. This allows us to commit our changes in stages and capture changes in logical portions rather than only large batches. For example, suppose we’re adding a few citations to relevant research to our thesis. We might want to commit those additions, and the corresponding bibliography entries, but not commit some of our work drafting the conclusion (which we haven’t finished yet).
To allow for this, Git has a special staging area where it keeps track of things that have been added to the current changeset but not yet committed.
Staging Area
If you think of Git as taking snapshots of changes over the life of a
project, git add specifies what will go in a
snapshot (putting things in the staging area), and
git commit then actually takes the snapshot, and
makes a permanent record of it (as a commit). If you don’t have anything
staged when you type git commit, Git will prompt you to use
git commit -a or git commit --all, which is
kind of like gathering everyone to take a group photo! However,
it’s almost always better to explicitly add things to the staging area,
because you might commit changes you forgot you made. (Going back to the
group photo simile, you might get an extra with incomplete makeup
walking on the stage for the picture because you used
-a!).
In the context of creating official statistics, using
--all or -a can lead to files being staged and
committed that should not be released (like microdata) or can cause
difficulties for others on the project (like environment files).
Staging things manually or using a pattern is the best practice, otherwise you might find yourself searching for “git undo commit” more than you would like!
Remember to use git status after you add files to check
what you have staged/added.
Let’s watch as our changes to a file move from our editor to the staging area and into long-term storage. First, we’ll add another line to the file:
OUTPUT
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite color
The two moons may be a problem for Wolfman
But the Mummy will appreciate the lack of humidityOUTPUT
diff --git a/mars.txt b/mars.txt
index 315bf3a..b36abfd 100644
--- a/mars.txt
+++ b/mars.txt
@@ -1,2 +1,3 @@
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite color
The two moons may be a problem for Wolfman
+But the Mummy will appreciate the lack of humiditySo far, so good: we’ve added one line to the end of the file (shown
with a + in the first column). Now let’s put that change in
the staging area and see what git diff reports:
There is no output: as far as Git can tell, there’s no difference between what it’s been asked to save permanently and what’s currently in the directory. However, if we do this:
OUTPUT
diff --git a/mars.txt b/mars.txt
index 315bf3a..b36abfd 100644
--- a/mars.txt
+++ b/mars.txt
@@ -1,2 +1,3 @@
Cold and dry, but everything is my favorite color
The two moons may be a problem for Wolfman
+But the Mummy will appreciate the lack of humidityit shows us the difference between the last committed change and what’s in the staging area. Let’s save our changes:
OUTPUT
[main 005937f] Discuss concerns about Mars' climate for Mummy
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)check our status:
OUTPUT
On branch main
nothing to commit, working tree cleanand look at the history of what we’ve done so far:
OUTPUT
commit 005937fbe2a98fb83f0ade869025dc2636b4dad5 (HEAD -> main)
Author: Vlad Dracula <vlad@tran.sylvan.ia>
Date: Thu Aug 22 10:14:07 2013 -0400
Discuss concerns about Mars' climate for Mummy
commit 34961b159c27df3b475cfe4415d94a6d1fcd064d
Author: Vlad Dracula <vlad@tran.sylvan.ia>
Date: Thu Aug 22 10:07:21 2013 -0400
Add concerns about effects of Mars' moons on Wolfman
commit f22b25e3233b4645dabd0d81e651fe074bd8e73b
Author: Vlad Dracula <vlad@tran.sylvan.ia>
Date: Thu Aug 22 09:51:46 2013 -0400
Start notes on Mars as a baseWord-based diffing
Sometimes, e.g. in the case of the text documents a line-wise diff is
too coarse. That is where the --color-words option of
git diff comes in very useful as it highlights the changed
words using colors.
Paging the Log
When the output of git log is too long to fit in your
screen, git uses a program to split it into pages of the
size of your screen. When this “pager” is called, you will notice that
the last line in your screen is a :, instead of your usual
prompt.
- To get out of the pager, press Q.
- To move to the next page, press Spacebar.
- To search for
some_wordin all pages, press / and typesome_word. Navigate through matches pressing N.
Limit Log Size
To avoid having git log cover your entire terminal
screen, you can limit the number of commits that Git lists by using
-N, where N is the number of commits that you
want to view. For example, if you only want information from the last
commit you can use:
OUTPUT
commit 005937fbe2a98fb83f0ade869025dc2636b4dad5 (HEAD -> main)
Author: Vlad Dracula <vlad@tran.sylvan.ia>
Date: Thu Aug 22 10:14:07 2013 -0400
Discuss concerns about Mars' climate for MummyYou can also reduce the quantity of information using the
--oneline option:
OUTPUT
005937f (HEAD -> main) Discuss concerns about Mars' climate for Mummy
34961b1 Add concerns about effects of Mars' moons on Wolfman
f22b25e Start notes on Mars as a baseYou can also combine the --oneline option with others.
One useful combination adds --graph to display the commit
history as a text-based graph and to indicate which commits are
associated with the current HEAD, the current branch
main, or [other Git references][git-references]:
OUTPUT
* 005937f (HEAD -> main) Discuss concerns about Mars' climate for Mummy
* 34961b1 Add concerns about effects of Mars' moons on Wolfman
* f22b25e Start notes on Mars as a baseDirectories
Two important facts you should know about directories in Git.
- Git does not track directories on their own, only files within them. Try it for yourself:
Note, our newly created empty directory spaceships does
not appear in the list of untracked files even if we explicitly add it
(via git add) to our repository. This is the
reason why you will sometimes see .gitkeep files in
otherwise empty directories. Unlike .gitignore, these files
are not special and their sole purpose is to populate a directory so
that Git adds it to the repository. In fact, you can name such files
anything you like.
- If you create a directory in your Git repository and populate it with files, you can add all files in the directory at once by:
Try it for yourself:
BASH
$ touch spaceships/apollo-11 spaceships/sputnik-1
$ git status
$ git add spaceships
$ git statusBefore moving on, we will commit these changes.
To recap, when we want to add changes to our repository, we first
need to add the changed files to the staging area (git add)
and then commit the staged changes to the repository
(git commit):
Choosing a Commit Message
Which of the following commit messages would be most appropriate for
the last commit made to mars.txt?
- “Changes”
- “Added line ‘But the Mummy will appreciate the lack of humidity’ to mars.txt”
- “Discuss effects of Mars’ climate on the Mummy”
Answer 1 is not descriptive enough, and the purpose of the commit is unclear; and answer 2 is redundant to using “git diff” to see what changed in this commit; but answer 3 is good: short, descriptive, and imperative.
Committing Changes to Git
Which command(s) below would save the changes of
myfile.txt to my local Git repository?
- Would only create a commit if files have already been staged.
- Would try to create a new repository.
- Is correct: first add the file to the staging area, then commit.
- Would try to commit a file “my recent changes” with the message myfile.txt.
Committing Multiple Files
The staging area can hold changes from any number of files that you want to commit as a single snapshot.
- Add some text to
mars.txtnoting your decision to consider Venus as a base - Create a new file
venus.txtwith your initial thoughts about Venus as a base for you and your friends - Add changes from both files to the staging area, and commit those changes.
The output below from cat mars.txt reflects only content
added during this exercise. Your output may vary.
First we make our changes to the mars.txt and
venus.txt files:
OUTPUT
Maybe I should start with a base on Venus.OUTPUT
Venus is a nice planet and I definitely should consider it as a base.Now you can add both files to the staging area. We can do that in one line:
Or with multiple commands:
Now the files are ready to commit. You can check that using
git status. If you are ready to commit use:
OUTPUT
[main cc127c2]
Write plans to start a base on Venus
2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 venus.txt
bio Repository
- Create a new Git repository on your computer called
bio. - Write a three-line biography for yourself in a file called
me.txt, commit your changes - Modify one line, add a fourth line
- Display the differences between its updated state and its original state.
If needed, move out of the planets folder:
Create a new folder called bio and ‘move’ into it:
Initialise git:
Create your biography file me.txt using
nano or another text editor. Once in place, add and commit
it to the repository:
Modify the file as described (modify one line, add a fourth line). To
display the differences between its updated state and its original
state, use git diff:
Content from Exploring History
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 25 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I identify old versions of files?
- How do I review my changes?
- How can I recover old versions of files?
Objectives
- view commit history of a file
- checkout an older version of a file
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Ignoring Things
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I tell Git to ignore files I don’t want to track?
- What do we have to watch for when creating official statistics?
Objectives
- create a .gitignore
- identify file types and areas of risk for official statistics
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Remotes in GitLab/GitHub
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 45 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I share my changes with others on the web?
Objectives
- Connect Git to a remote repository
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Collaborating
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 35 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I use version control to collaborate with other people?
Objectives
- Use Git and branches to work with others locally
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Conflicts
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 15 minutes
Overview
Questions
- What do I do when my changes conflict with someone else’s?
Objectives
- Resolve a merge conflict
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Working with Others in GitHub/GitLab
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 20 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I put work on the protected branch?
- How can we keep track of what needs to be done?
- How can I add collaborators?
Objectives
- Add collaborators to a remote repository
- use issues to keep track of project needs
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Documenting in GitHub/GitLab for official statistics
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I create documentation so others can understand my methodology?
- How can I host it easily on GitHub?
Objectives
- Create documentation using markdown
- add links and images to documentation
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
Content from Citation
Last updated on 2024-07-11 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 5 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I make my work easier to cite?
Objectives
- How to cite and be cited
Welcome to using Git in Official Statistics!
- First key point. Brief Answer to questions. (FIXME)
